Author: Mike Peña
-
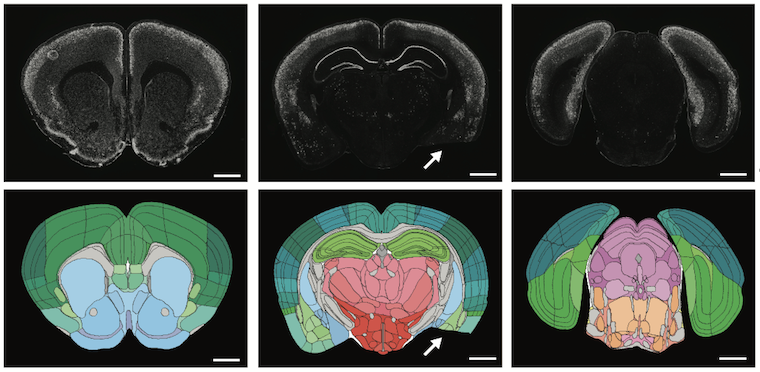
Student-built app slashes weeks off brain mapping to speed up neuroscience research
UC Santa Cruz neuroscientists aiming to better understand how specific brain connectivity contributes to perception, thoughts, and behavior are leveraging artificial intelligence to enhance their study of brain function. By integrating AI, they are streamlining the process of aligning thin slices of mouse brain tissue with a reference atlas, helping to identify key details such…
-

Explaining how our biological clocks work and how to better regulate our circadian rhythms
As anticipation builds for the longer days that follow this weekend’s switch to daylight savings time, the moment seemed ideal to turn to one of the nation’s leading circadian-rhythms researchers, UC Santa Cruz’s Carrie Partch.
-

New biology study reveals four novel genes required for male fertility in mice
The pioneering research of UC Santa Cruz’s Upasna Sharma to determine how a father’s life experiences and environment can influence the health and wellbeing of his children moves forward with the recent discovery of four genes required for male fertility and the creation of specific RNA molecules in sperm.
-

Astrophysicist explores interconnectedness of art and science
A new book by UC Santa Cruz astrophysicist and visual artist Nia Imara debuts tomorrow that explains the universe and traces how art has blended with science throughout human history.
-
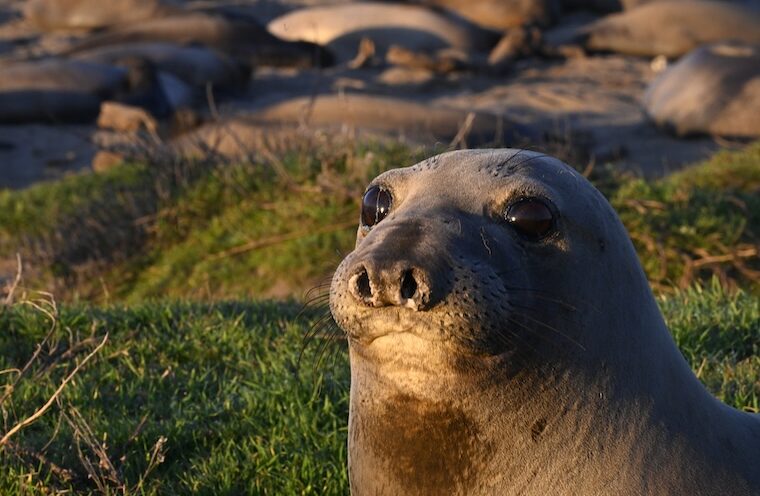

Foraging seals enable scientists to measure fish abundance across the vast Pacific Ocean
A new study led by UC Santa Cruz marine biologist Roxanne Beltran to be published as the February 14 cover story for Science concludes that seals can essentially act as “smart sensors” for monitoring fish populations in the ocean’s eerily dim “twilight zone.”
-
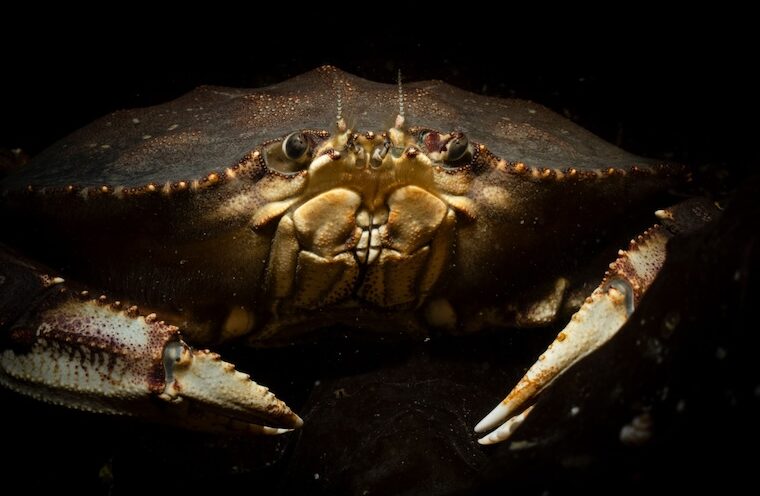

Economically, culturally important marine species vulnerable to changing climate, new study shows
Dungeness crab, Pacific herring, and red abalone are among the marine species most vulnerable to the changing climate’s effect on California’s coastal waters, a new study led by UC Santa Cruz researchers finds.
-
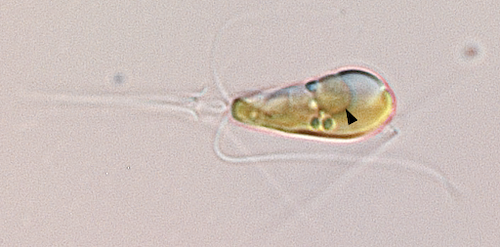
AAAS names UC Santa Cruz organelle discovery most outstanding paper in 2024
The discovery by UC Santa Cruz researchers of a new organelle within single-celled algae that converts nitrogen gas into ammonia continues to be celebrated by the science community, this time by winning the prestigious AAAS Newcomb Cleveland Prize.
-
Students make winning videos about importance of federal support for science research
Impactful scientific discovery isn’t possible without funding to support the research, and three UC Santa Cruz students have created short videos that took top prizes in a national competition held by the Science Coalition, a nonprofit, nonpartisan organization dedicated to sustaining the federal government’s investment in basic scientific research.
-
Hubble Telescope images combined into giant mosaic of neighboring Andromeda Galaxy
Astronomers are celebrating the completion of a 2.5-billion-pixel panoramic picture of the entire Andromeda Galaxy. The team includes several UC Santa Cruz researchers who made significant contributions to the enormous photomosaic that combines some 600 snapshots taken by the Hubble Space Telescope over more than a decade and 1,000 orbits.
-

American Astronomical Society honors four UC Santa Cruz affiliates at national meeting
At this week’s AAS national meeting, the society named UC Observatories Director Bruce Macintosh and two alumni, Laura Lopez and Mark Phillips, among the 24 new fellows chosen for 2025.
-
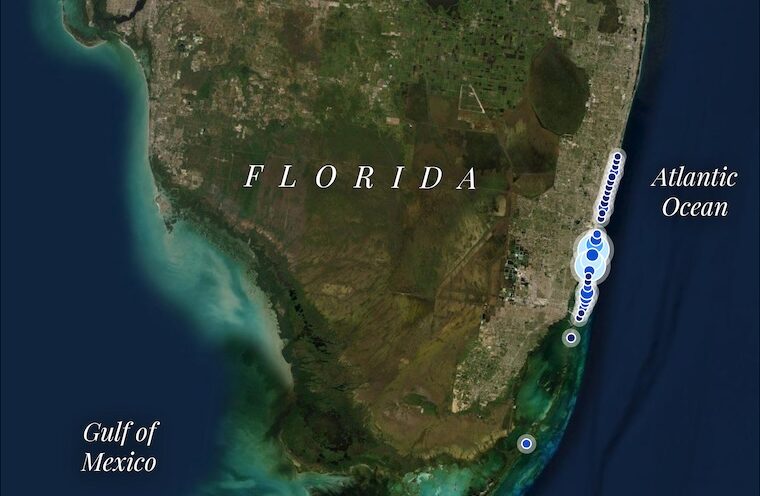
Coral-reef restoration can be cost-effective for saving lives, money
A new study co-led by the Center for Coastal Climate Resilience (CCCR) at UC Santa Cruz shows coral reef restoration in Florida and Puerto Rico could save thousands of lives and prevent hundreds of millions of dollars in damage and economic interruption each year.
-
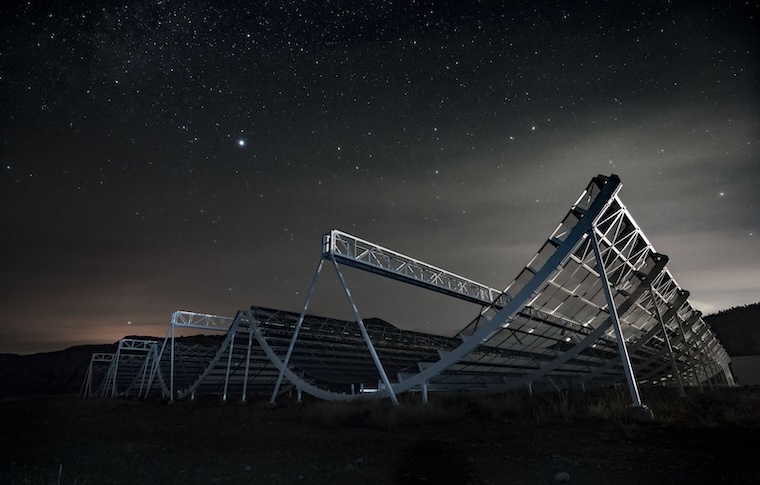

Researchers link mysterious cosmic signals to collapsed stars
An international team of scientists has provided the clearest evidence yet that some fast radio bursts (FRBs)—enigmatic, millisecond-long flashes of radio waves from space—originate from neutron stars, the ultra-dense remnants of massive stars that have exploded in a supernova.